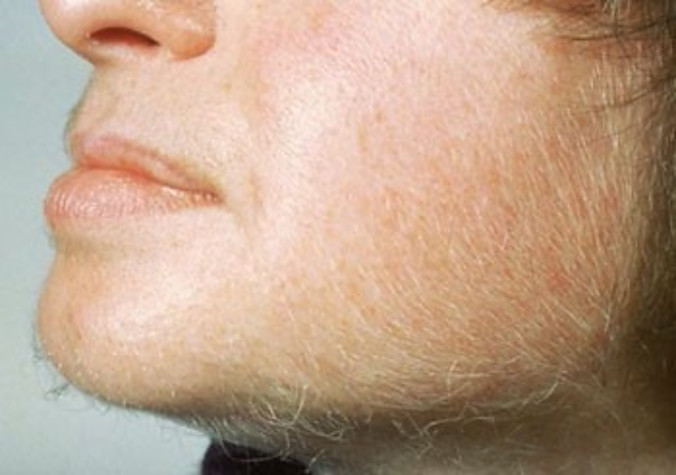
Definition: Hirsutism is a condition of unwanted, male-pattern hair growth in women. Hirsutism may arise from excess male hormones called androgens, the key hormone being testosterone. It may also be due to an ethnic or family trait. Up to 10 percent of U.S. women have some degree of hirsutism. [1]
Symptoms and Signs
The major sign of hirsutism is coarse and pigmented body hair, appearing on places of the body where hair is not commonly found in women (chest, lips, ect). Signs of hirsutism may also include:
- A deepening voice
- Balding
- Increasing acne
- Decreased breast size
- Enlargement of the clitoris
- Increased muscle mass [1]
Causes
Hirsutism usually results from excess androgens, but can also be due to increased sensitivity of hair follicles to androgens. Half of the women with mild hirsutism have high androgen levels, and this usually causes severe hirsutism. There are several conditions that can cause high androgen levels. Some of these include:
Cushing’s syndrome – Cushing’s syndrome is a condition that occurs when your body is exposed to high levels of the hormone cortisol (steroid hormone). This is usually released when the body responds to stress. [1] Cushings develops when your adrenal glands make too much cortisol or if you take cortisol-like medications over a long period of time which disrupts the balance of sex hormones in your body.
Polycystic ovary syndrome – This is a common condition caused by an imbalance of sex hormones. Symptoms of this include irregular periods, infertility and sometimes multiple cysts on the ovaries. Polycystic ovary syndrome is the most common identifiable cause of hirsutism. [1]
Other less common causes of hirsutism include tumors (usually androgen secreting) and medications such as danazol, which is used to treat women with endometriosis. [1] Excessive hair growth in women with normal androgen levels, regular menstrual periods and no other underlying conditions is called idiopathic hirsutism, meaning that there’s no identifiable cause of the disorder. [1] This occurs more frequently in Mediterranean, Middle Eastern and South Asian ethnic populations. [1]
When to seek medical advice
See your doctor if you develop unwanted hair on locations in odd locations such as your upper lip, midchest, inner thighs or low back Esepcially if you have irregular periods, and have just begun on a new medication and notice these symptoms. Women approaching menopause or in the early years of menopause may develop coarse chin or other unwanted facial hair, but this isn’t considered hirsutism. [1]
Treatment Options
Laser Hair removal – Laser hair removal is the use of laser energy to produce long-term hair reduction. The heat from the light of the laser is absorbed by the pigment, or melanin, in the hair. That heat then triggers inflammation in the hair follicle, which causes the follicle to go into its resting (telogen) phase. While resting, the follicle produces no hair. [2]
Advantages – Laser hair removal is a non-invasive method of photoepilation, which does not require needles or chemical creams. The advantages of laser hair removal include:
1. The technique is safe if performed properly.
2. It is considered to be less painful as compared to other methods
3. Many consumers have experienced long-lasting hair removal or even permanent hair reduction
4. The method is very useful for removing hair from large areas such as backs or legs. For example, to remove hair from the back with laser hair removal usually takes about an hour. In contrast, a full back hair removal with electrolysis can take up to and over 125 hours. [2]
Disadvantages – Some patients may experience hair regrowth. However, this hair is usually finer and lighter in color. Possible side effects, though very rare, may include damage to the surrounding healthy tissue in the form of scars, burns, redness and swelling. The process is also not as effective on unpigmented (gray) hairs and red or blonde hair. [2]
At Home Laser Hair Removal – Another great option for laser hair removal is the FDA-cleared at-home laser hair removal system. About the size of a small hair dryer, this hand-held device is based on the same technology behind the LightSheer diode laser preferred by physicians worldwide. The TRIA Laser Hair Removal System is one device for home hair removal that works by targeting the dark pigment (melanin) in the hair to generate heat that disables each follicle. For added safety, the power levels are gently reduced, which means treatment takes a little longer but the results are the same as doctor’s office hair removal treatments. After 2 months you will see hair lighten and become finer, and after 3 months there will be a visible reduction in the amount of regrowth. [2]
Most people benefit from a series of three to seven hair removal treatments, spaced at four- to eight-week intervals. After the initial series of treatments, the hair in a given area is usually reduced in both amount and thickness for a very long period of time. However, it may not be completely gone. To keep an area completely devoid of hair, maintenance treatments are almost always required. Fortunately, maintenance treatments can usually be administered at ever-increasing intervals. Eventually, they may be needed only once a year, or even less often.
Electrolysis – This type of therapy involves inserting a tiny needle into each hair follicle and emitting a pulse of electric current to damage and eventually destroy the follicle. Electrolysis results in permanent hair removal, but the procedure can be painful. Some numbing creams may be spread on your skin to reduce this discomfort. Side effects include lightening or darkening of the treated skin and rarely, scarring. [3]
Medical Therapies
Anti-androgens – These types of drugs block androgens from attaching to their receptors in your body. The most commonly used anti-androgen for treating hirsutism is spironolactone (Aldactone). [1]
Oral contraceptives – Birth control pills contain the hormones estrogen and progestin inhibit androgen production by your ovaries. [1]
Topical cream – Eflornithine (Vaniqa) is a prescription cream specifically for excessive facial hair in women. [1] This is applied to the skin to slow new hair growth. It does not remove existing hair and may take up to two months to work. Also growth returns if you stop using the medication. Side effects may include stinging, tingling or a skin rash. [1]
Home Remedies
Plucking – Using a tweezers is a good method to remove a few stray hairs, but is not useful for removing a large area of hair. This is the most common method women use to get rid of unwanted facial hair. [3]
Shaving – Shaving is quick and inexpensive, but it needs to be repeated on a regular basis since it removes the hair only down to the surface of your skin, and does not stop hair from growing back. [3]
Waxing – Waxing (applying warm wax in the area of unwanted hair and pulling back from the skin against the direction of hair growth) removes hair from a large area quickly. This may sting temporarily and cause skin irritation and redness. Hot wax can also burn your skin. [3]
Chemical depilatories – These are topicals to spread on the skin and work by breaking down the protein structure of the hair shaft. [3] Some people are allergic to the chemicals used in depilatories, and these may cause rashes. They often also smell bad.
Bleaching – Instead of removing unwanted body hair, some women bleach the hair to a lighter color. Bleaching removes the hair pigment, so the hair is less visible against the surface of your skin. Bleaching may cause skin irritation. [1]
References
- Hirsutism. http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/hirsutism/DS00858
- Laser Hair Removal Journal. The Patient’s Guide. http://www.hairremovaljournal.org/whatislhr.aspx
- Hirsutism. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1072031-overview






































